class ii elastics effect
Finite element models that simulate the effects of class II elastics on the mandibular arch in six different scenarios using various immobilization methods of the posterior dentition were studied. These elastics help move your upper teeth back and your bottom teeth forward.
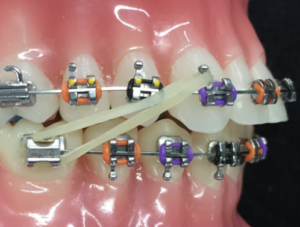
Are Class Ii Elastics As Effective As A Functional Appliance A Trial That May Answer This Question Kevin O Brien S Orthodontic Blog
Extrusion of upper incisors.

. To investigate the effect of Class II intermaxillary elastics on the functional occlusal plane FOP of growing patients. They tip and extrude the maxillary incisors. En-mass movement non extraction - class 2 3 elastics 5-6 ounces 142-170g.
The following are the effects of Class 2 elastics. We show you in this video demonstration exactly how its done. Forsus group mean age 1419 102 years and elastics group.
Watch and learn more. Buccal tipping of lower incisors forward movement of the entire mandibular arch. Finite Element Models that simulate the effects of Class II elastics on the mandibular arch in six different scenarios using various immobilization methods of the posterior dentition were studied.
To compare the effectiveness of comprehensive fixed appliance treatments implemented in combination with Forsus or intermaxillary elastics in Class II subdivision subjects. To evaluate the skeletal dentoalveolar and soft tissue effects of skeletally anchored Class II elastics and compare them with a matched control group treated by a monobloc appliance. Class II elastics are designed to exert an anteroposterior force on maxillary teeth and a postero-anterior force on the mandibular arch.
Class II elastics are effective in correcting Class II malocclusions and their effects are mainly dentoalveolar including lingual tipping retrusion and extrusion of the maxillary incisors. This article can only be viewed by JCO subscribers. A ppliances designed for Class II correction generate either pulling interarch force vectors intermaxillary elastics or pushing interarch force vectors bite-jumping devices.
For a class 2 you will want to connect your elastic from upper 3 down to the lower 6. Individual patient growth pattern must be taken into consideration when treatment planning the use of Class II elastics. Maximum strain on the PDL and maximum stress on alveolar bone increased with.
Those mechanics helped to extrude the molars intrude and procline the incisors and facilitate further mandibular growth. The mandibular incisors were protruded in the monobloc group 545 123 whereas they were retruded in the elastics group -301 166. 4 rows Class II elastics are effective in correcting Class II malocclusions and their effects.
It is very important to know the side effects of Class II elastics before using them in an orthodontic treatment. Anterior elastics box elastic for anterior openbite 1-2 ounces 28-57g. Extrusion of lower first molar.
En-mass movement extraction class 2 3 elastics 4-5 ounces 113-142g. Neither skeletal pattern nor treatment modality differed in the response to Class II elastics with regard to FOP changes. As the present case shows when Class II elastics are.
JULIEN PHILIPPE DCD DSO. The class II elastics have different effects6. Mechanical Analysis of Class II Elastics.
The following are the effects of Class 2 elastics. Upper incisor extrusion Lower first molar extrusion Lower incisor flaring Distal movement of the upper teeth and mesial movement of the lower teeth Steepening of the occlusal plane. The undesirable dentoalveolar effects of the monobloc appliance were eliminated by using miniplate anchorage.
Flaring of the lower incisors. Are Class II elastics7 In spite of their popularity8 some authors have attributed several side effects to the use of Class II elasticseg loss of mandibular anchorage proclination of mandibular incisors extrusion of maxil-lary incisors and even worsened smile esthetics because of increased gum exposurethus suggesting minimal. The primary effect of the Class II elastics is the significant sagittal change in the cuspid.
Twenty-eight Class II subdivision patients were allocated to two groups using matched randomization. Effects upon the mandibular arch. Because the force is usually not parallel to the occlusal plane.
1 Intermaxillary elastics which have the capacity to produce both sagittal and extrusive forces at the point of attachment are the most popular mechanism for correction of sagittal problems. For a class 3 you will want to connect from the upper 6 down to the lower 3. This depends on the clinical situation.
Maximum strain on the PDL and maximum stress on. A total of 50 participants aged 11 to 16 years were selected from a university clinic archive 1-year after treatment and after undergoing 6 months of Class II elastic wear taking pretreatment T0 and posttreatment T1. Posterior box elastics 6 ounces 170g.
Effects upon the maxillary archupper incisors are more vertical extrusion and downward movement of anterior occlusal plane backward movement of the upper arch dental distalization. Multiple studies have reported a lack of strong evidence that the use of Class II elastics results primarily in negative side effects as was previously suggested. Distal movement of the upper teeth and mesial movement of the lower teeth.
Per-element distribution of linear elastic stress-strain and total displacement were computed. Below are the side effects of Class II elastics. Class II elastics are effective in correcting Class II malocclusions and their effects are mainly dentoalveolar including lingual tipping retrusion and extrusion of the maxillary incisors.
Favorable skeletal outcomes can be achieved by skeletal anchorage therapies which could be an. Animation demonstrating the use of Class II elastics. Want to license our anima.
Class II elastics are auxiliary forces that can be classified as active elements in a fixed appliance system1 They have been used in the correction of Class II malocclusion since the early days of orthodontic treatment26 although some undesirable effects can occur depending on their vertical force vectors4610 The vertical force can extrude the mandibular molars and. Per-element distribution of linear elastic stress-strain and total displacement was computed. Use of Class II elastics during the growth period was not found to show adverse effects on FOP rotation.
Five Star Orthodontic Lab and supply has been servicing the Orthodontic community for over 30 years.

Direction Of Force For Class Ii Correction A Class Ii Elastics With Download Scientific Diagram

Class Iii Elastic On The Right Side Anterior Diagonal Elastic And Download Scientific Diagram

Class Ii Elastics Using The Lower Miniscrews As Anchorage And Download Scientific Diagram

How To Put Rubber Bands On Braces Premier Orthodontics

Long And Short Class Ii Elastics Youtube
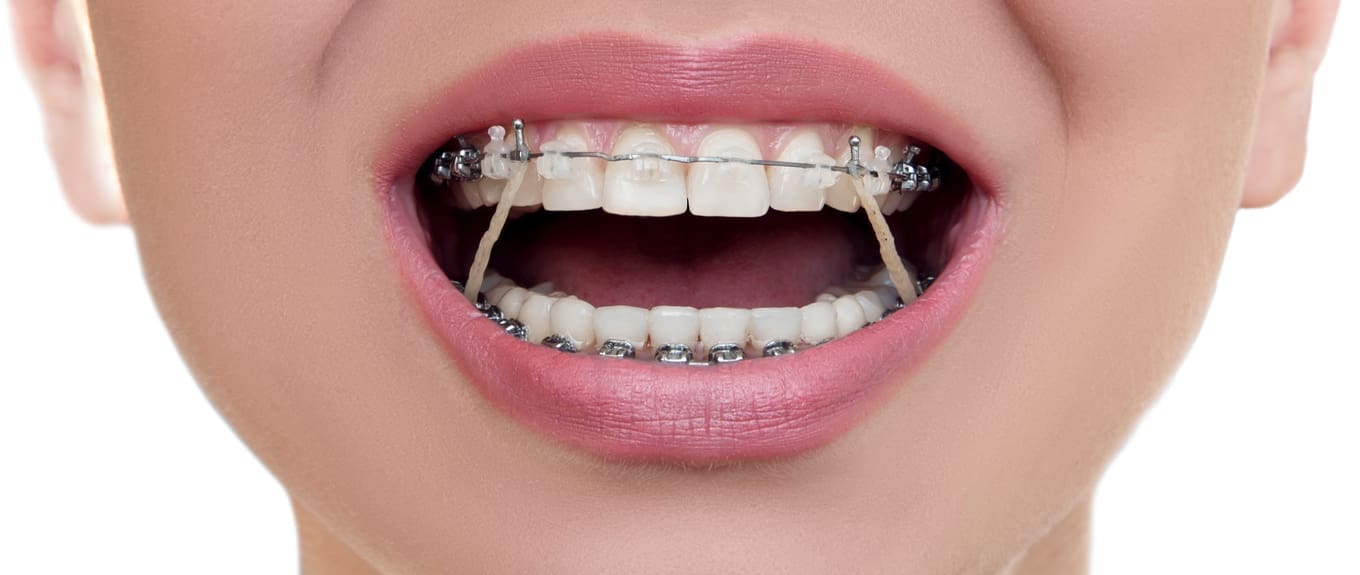
Are Class Ii Elastics As Effective As A Functional Appliance A Trial That May Answer This Question Kevin O Brien S Orthodontic Blog

Effects Of Skeletally Anchored Class Ii Elastics A Pilot Study And New Approach For Treating Class Ii Malocclusion Semantic Scholar

How To Put Rubber Bands On Braces Premier Orthodontics
Treatment Of Class Ii Division 1 Malocclusion With Class Ii Elastics
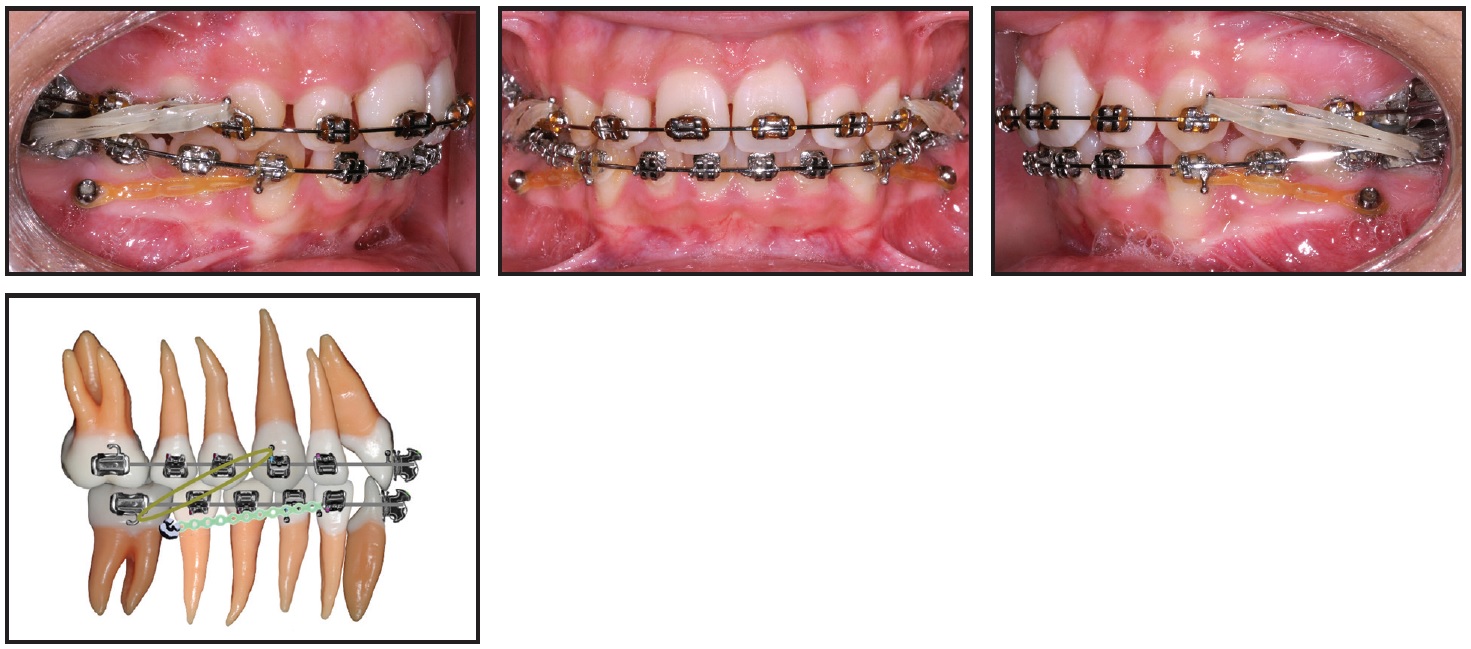
Case Report Jco Online Journal Of Clinical Orthodontics

Class Ii Elastics Lateral View Hd Edition Youtube
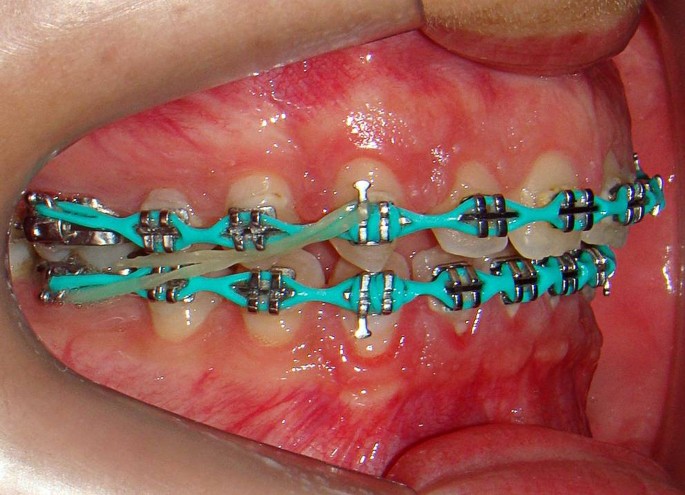
Soft Tissue Profile Changes In Angle Class Ii Patients Treated With Twin Force Or Intermaxillary Elastics A Comparison Springerlink

Mid Treatment Intraoral Photographs With Class Ii Elastics Download Scientific Diagram
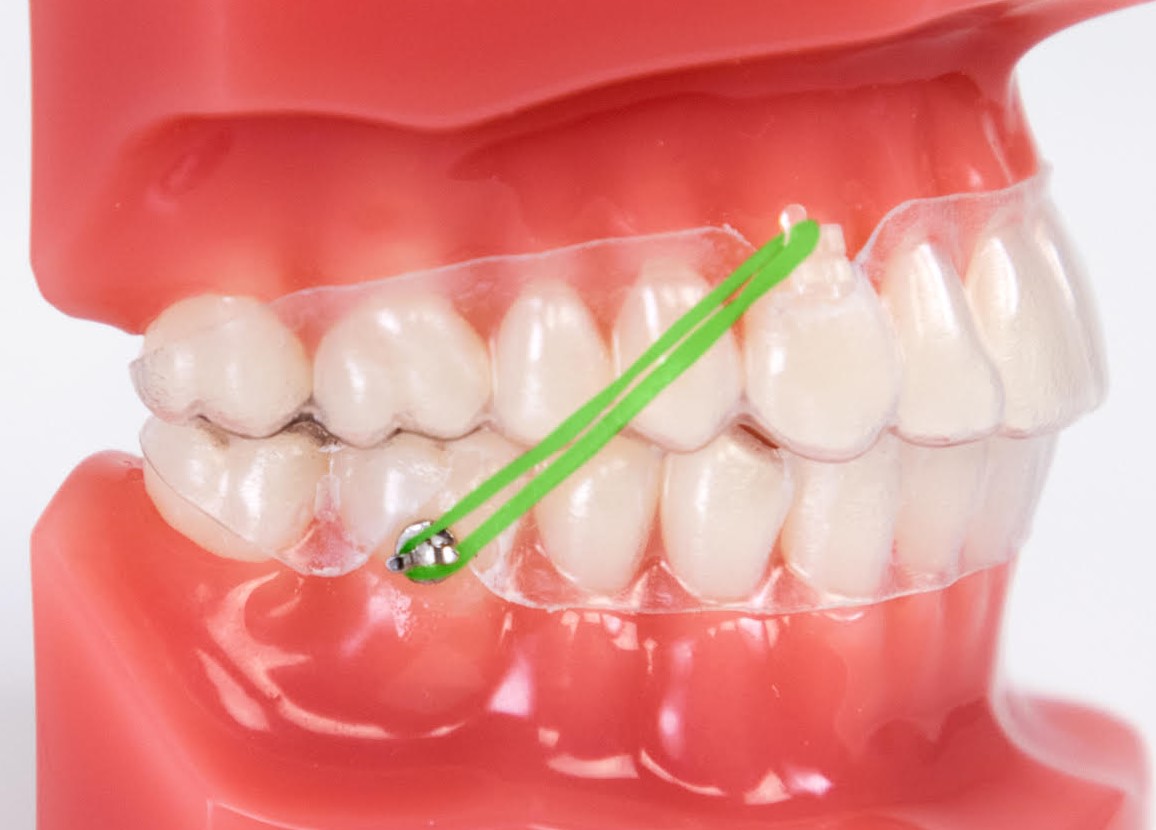
Arch Correction Simulation Acs Clearcorrect Support

Figure 4 From The Effect Of Intermaxillary Elastics In Orthodontic Therapy Semantic Scholar

